Haga clic aquí para la versión en español.
The Beauty and Meaning of Catholic Architecture: A Journey Through Sacred Spaces
Catholic architecture is more than just a collection of buildings; it is a profound expression of faith, theology, and tradition. From the grand cathedrals of Europe to humble chapels in remote villages, Catholic architecture tells the story of a faith that has shaped civilizations for over two millennia. This blog explores the history, styles, and spiritual significance of Catholic architectural design.
 A Historical Overview
A Historical Overview
Catholic architecture has evolved over the centuries, influenced by cultural, artistic, and theological developments. Each era has left its mark, reflecting both continuity and innovation within the Church.
Early Christian and Romanesque Architecture
The earliest Christian places of worship were simple house churches, often adapted from existing Roman buildings. By the fourth century, following Emperor Constantine’s Edict of Milan (313 AD), Christianity became legally recognized, leading to the construction of the first basilicas. These structures, such as the Basilica of St. John Lateran in Rome, featured long nave spaces, clerestory windows, and apse-focused designs to highlight the altar.
During the Romanesque period (10th–12th century), churches became more robust and fortress-like, characterized by thick walls, rounded arches, and barrel vaults. These features provided both structural stability and a sense of solemnity. Famous examples include the Basilica of Saint-Sernin in Toulouse and Speyer Cathedral in Germany.
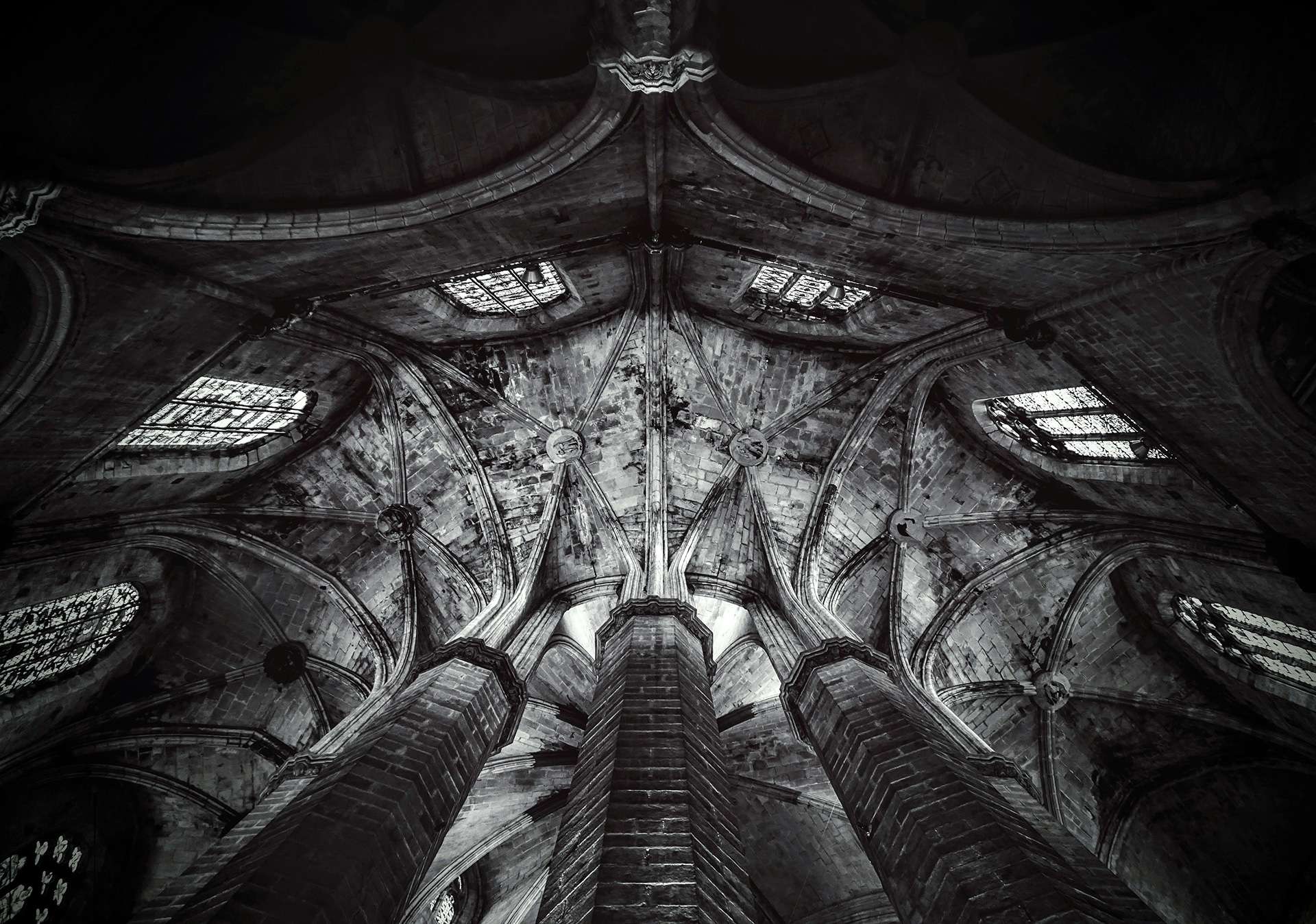
Gothic Splendor: Reaching Toward Heaven
The Gothic era (12th–16th century) introduced soaring spires, pointed arches, and ribbed vaults, creating a sense of verticality that directed the viewer’s gaze toward Heaven. Stained-glass windows, such as those in Chartres Cathedral, depicted biblical stories in dazzling color, transforming interiors into sacred storytelling spaces. Flying buttresses, a hallmark of Gothic design, allowed for larger windows and thinner walls, making the church interiors brighter and more ethereal.
Renaissance and Baroque Grandeur
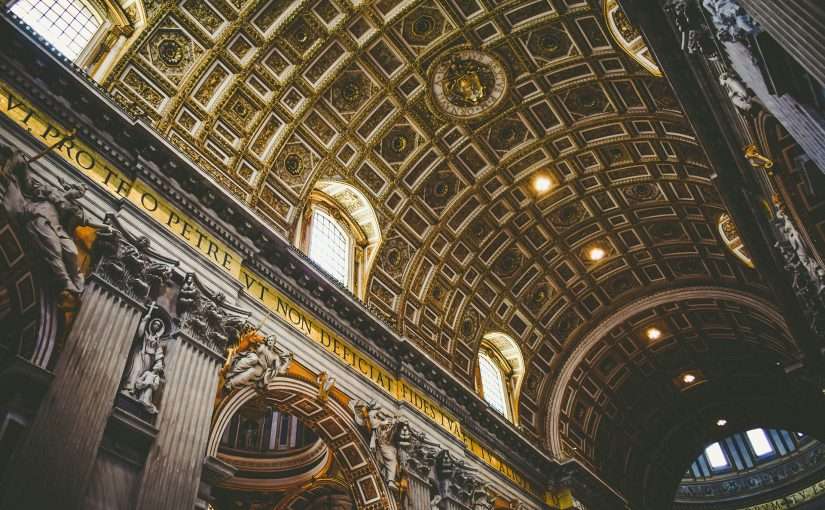
The Renaissance (15th–17th century) ushered in a return to classical harmony, symmetry, and proportion, inspired by ancient Roman and Greek architecture. St. Peter’s Basilica in Vatican City, with its majestic dome designed by Michelangelo, exemplifies this period’s architectural mastery.
The Baroque period (17th–18th century) followed, emphasizing movement, dramatic contrasts, and ornate decoration. Catholic churches from this era, such as the Church of Gesù in Rome, utilized illusionistic frescoes, elaborate altarpieces, and theatrical lighting to create an overwhelming sense of divine presence.
Neoclassicism to Modern Interpretations
By the 18th and 19th centuries, Neoclassical designs emerged, emphasizing simplicity, symmetry, and grandeur without excessive ornamentation. The 20th and 21st centuries brought modernist and postmodern approaches, where architects experimented with new materials and forms while still seeking to convey Catholic theological truths. Examples include Le Corbusier’s Chapel of Notre Dame du Haut in France and Santiago Calatrava’s Cathedral of Our Lady of the Angels in Los Angeles.
Symbolism and Theological Significance
Catholic architecture is deeply symbolic, designed to lead the faithful from the earthly realm into the presence of God. Key elements include:
- The Cruciform Layout: Many Catholic churches are built in the shape of a cross, symbolizing Christ’s sacrifice and inviting worshippers into a sacred narrative.
- The Sanctuary and Altar: As the focal point of Catholic worship, the sanctuary represents Heaven, with the altar as the place of Christ’s sacrifice in the Eucharist.
- Stained Glass Windows: These serve both an educational and spiritual function, illuminating biblical events and the lives of saints.
- The Dome and Verticality: The dome represents the heavens, while soaring ceilings and spires direct the soul toward God.
- Sacred Art and Statues: Depictions of Christ, the Virgin Mary, and the saints inspire devotion and reflect the Communion of Saints.
Regional Variations in Catholic Architecture
Catholic architectural styles vary across cultures, incorporating local artistic traditions while maintaining universal themes.
- European Catholicism: Gothic cathedrals like Notre-Dame de Paris and St. Patrick’s Cathedral in New York represent the height of medieval Catholic expression.
- Latin American Catholicism: Spanish Baroque churches, such as Mexico City’s Metropolitan Cathedral, blend indigenous and European elements.
- Asian Catholicism: In countries like the Philippines and India, churches incorporate native motifs alongside traditional Catholic structures.
- African Catholicism: Modern African Catholic architecture often integrates local materials and artistic expressions to create a unique blend of tradition and innovation.
Catholic Architecture in Contemporary Worship
Modern Catholic architecture continues to evolve while staying rooted in tradition. Contemporary churches balance innovation with spiritual significance, using minimalist designs, sustainable materials, and new technology to create spaces that facilitate worship and community gathering. Architects now consider environmental sustainability, integrating natural light, acoustics, and adaptable spaces for a modern congregation.
Conclusion: A Living Tradition
Catholic architecture is not just about aesthetics; it is a theological and spiritual journey in stone, glass, and light. It reflects the Church’s mission to uplift the human spirit and bring the faithful closer to God. Whether in grand cathedrals or simple chapels, Catholic architecture continues to inspire awe, communicate sacred truths, and stand as a testament to a faith that has endured through the ages.