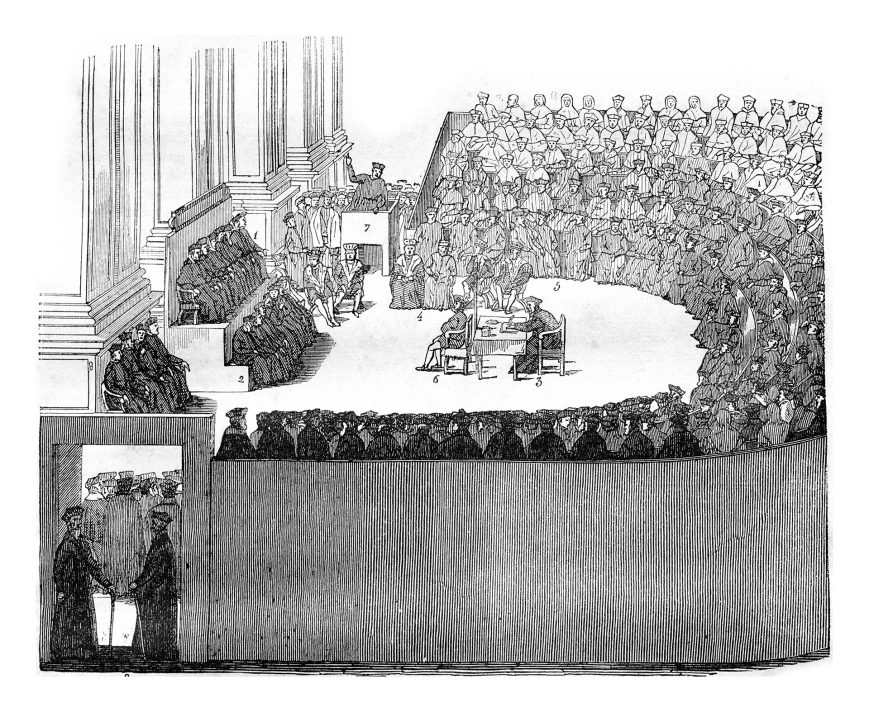
Occasioned by the Protestant Reformation, the Council of Trent, through catholic clergymen, formulated the Roman Catholic church’s arguments against the reformation.
The reformation was a religious revolution against the Roman Catholic Church and was mainly championed by Martin Luther and John Calvin.
As such, the Council of Trent was, in a sense, a formal reply to the doctrinal teachings contested by the early Protestant movement.
Through the council, the clergymen were able to define what the Catholic Church would be like in the coming years.
In addition to this, the members of the council covered key agendas that were affecting the Roman Catholic Church as of that time.
The Council of Trent has great significance to the history of the Roman Catholic Church. And even though the council had its last meeting in 1563, the matters that were discussed still guide the modern-day catholic church.
Here are the top five things that you probably didn’t know about the Council of Trent:
1. It Was The Apex of The Roman Catholic’s Counter-Reformation
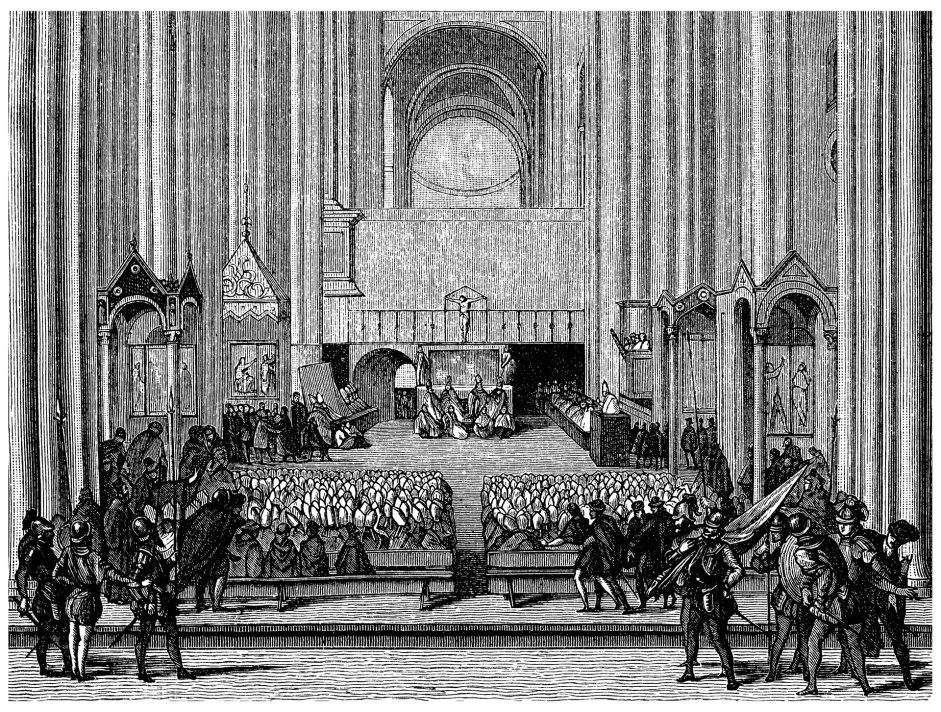
 During the Reformation period, the Roman Catholic Church faced a lot of opposition from the protestants.
During the Reformation period, the Roman Catholic Church faced a lot of opposition from the protestants.
According to protestants, certain teachings of the early catholic church were not in line with the divine words of the scripture.
Additionally, the protestants believed that the leaders of the Roman Catholic church were abusing the power invested in them by the church.
Aside from that, Protestantism questioned some of the sacraments in the catholic church. As result, some members of Roman Catholicism left the church and joined Protestantism.
However, not all members of the catholic church converted to Protestantism when Martin Luther challenged the teachings of Catholicism.
Nonetheless, some Catholics still had doubts about certain doctrinal teachings and also questioned how the church was being managed.
In an attempt to unify the early Roman Catholic Church, Pope Paul III convened the Council of Trent by appointing a commission to analyze the operations of the Roman Catholic Church.
2. The Council of Trent Faced Internal Resistance
In as much as the council was convoked by the Pope himself, some members of the Roman Catholic church opposed it. As such, it faced both internal and external strife.
Since the main goal of the council was to reform the church, corrupt bishops and priests did not support the ideas that were being proposed by members of the council.
Also, the council did not meet as often since there was a lot of tension in the region. The meetings were often suspended or delayed, thus causing even more problems among the council members.
Plus, members of the council did not always agree on certain matters and this greatly affected the operations of the council.
3. The Council of Trent Was The Roman Catholic Church’s First Reply To Protestant Reformation
For years, the protestants challenged some of the key teachings of the Roman Catholic church. However, the church did not make a formal reply until the Council of Trent was convened.
Through the council, the clergymen were able to counter Protestant Reformation arguments that were against the teachings of the Roman Catholic Church.
In addition to this, the council encouraged adherents of the catholic church to refute all protestant teachings.
This allowed members of the Catholic church to fully commit to Catholicism and its teachings.
Consequently, the Roman Catholic church was able to retain most of its followers amid the Reformation.
4. It Strengthened Ecclesiastical Discipline In The Roman Catholic Church
Clergy abuse in the early Catholic church is one of the factors that led to the Protestant Reformation.
Martin Luther purported that clergymen in Roman Catholicism were driven by greed. As such, they exploited the poor and the less privileged, thus creating a split in the church.
To correct this, members of the council came up with new ways of training the clergy, thereby unifying the church and its leaders.
Each diocese was, in turn, required to provide its members with proper education before assigning any roles to the clergymen.
Additionally, the Council of Trent abolished the common forms of abuse in Catholicism.
Through this, the Roman Catholic began to function as a unit, hence attracting even more people to Christianity.
5. The Council of Trent Reinforced The Doctrinal Teaching of Salvation In Roman Catholicism
According to Protestantism, salvation is God’s will for all types of people and can be achieved through faith alone.
Contrarily, the Catholic church teaches that salvation can only be attained through faith and good works.
By basing their teachings on the Book of James 2:26 (NKJV; “For as the body without the spirit is dead, so faith without works is dead also”) members of the council reinforced the doctrinal teaching of salvation in Catholicism.
Thus, refuting the teaching of Protestantism on the same topic. This helped members of the catholic church to avoid unnecessary confusion when discussing matters pertaining to salvation.
How Did The Council Of Trent Try To Improve Priesthood?
The Council of Trent clarified a wide range of doctrines in Roman Catholicism. It particularly impacted the priesthood through the introduction of new rules that governed clergymen.
According to Martin Luther, all members of the church are priests, meaning they have equal responsibilities and rights when it comes to handling religious matters.
However, Catholicism teaches that priesthood is both universal and ministerial. The council of Trent somewhat acknowledged the existence of a universal priesthood but the only difference is that the clergymen had to go through religious training before they are ordained.
To clarify, the Council of Trent improved priesthood by:
Introducing Seminary Training For Priests
As a requirement, all catholic priests were to attend seminary school before they could serve in the church.
This allowed them to learn more about the scripture and everything that it stands for. In addition to this, they were taught about canon law, moral theology, and the meaning of the sacraments in the Roman Catholic Church.
Also, the priests learned liturgical theology and covered other religious subjects that could prepare them for their new roles in the church.
This is also another way through which the council strengthened discipline in the early Roman Catholic Church. That way, the priests were better suited for the roles that they were given by the church.
Reaffirming Holy Orders As a Sacrament
In the catholic church, the holy orders are considered sacraments. As such, those who are ordained as priests, deacons, or bishops are in fact taking part in one of the sacraments of Catholicism.
Unlike most sacraments in the catholic church, the holy order is not a sacrament that all members of the church can partake in.
The council members reaffirmed the holy orders on the twenty-third session in 1563, making this one of the key decisions that was made by the Council of Trent.
Major Objectives of The Council of Trent
The Council of Trent discussed different competing agendas that were affecting the Roman Catholic church and its members.
Nonetheless, the clergymen chairing the council had two main objectives in mind:
To make changes in the church’s leadership and other ideas that tainted the image of the Roman Catholic Church
The topic of justification was one of the commonly questioned religious teachings in the early Christian church.
Besides, Martin Luther’s doctrinal teachings challenged the ideas of the Roman Catholic church.
To counter this, the Council of Trent clearly defined the relationship between faith and actions and how they can lead one to salvation.
To refute and stop the spread of Protestantism Teachings
Since the Protestant Reformation was against most of the teachings in Roman Catholicism, the clergymen ensured the ideas of Protestantism did not spread among the members of the catholic church.
According to the Council of Trent, the church’s scriptural teachings were final and anybody who did not follow them was considered a dissident.
Additionally, the council reaffirmed that the church traditions and the divine scripture had the same religious authority in the church.
As such, the Roman Catholic church did not only retain but also protected its doctrinal teachings.
Final Verdict
The Council of Trent did not only clarify but as redefined the Roman Catholic church’s doctrines.
In addition to this, the council reformed the catholic church by making key leadership changes. Also, members of the Council of Trent made a great impact on the church’s teachings and beliefs.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Did The Council Of Trent Decide About The 7 Sacraments?
Like most teachings of the Roman Catholic church, the Council of Trent reaffirmed the seven sacraments.
When Did The Council Of Trent Begin?
The members of the Council of Trent had twenty-five sessions that were held from 13 December 1545 to 4 December 1563.
How Did The Council Of Trent Reform The Catholic Church?
The Council of Trent abolished ecclesiastical abuses, reaffirmed doctrines, and also strengthened papal supremacy in the early Roman Catholic church.

One thought on “5 Things You Maybe Didn’t Know About The Council of Trent”